1. Can you provide an overview of the current healthcare landscape, focusing on the role of government policies and insurance plans?
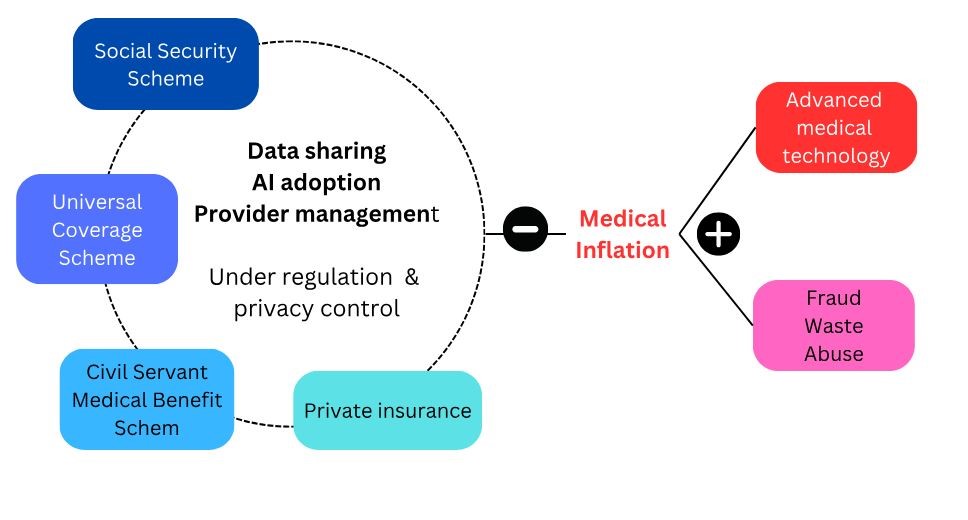
In Thailand, healthcare services are offered through a combination of public and private sectors. The primary public scheme, overseen by the National Health Security Office (NHSO), is the Universal Coverage Scheme (UCS), ensuring fundamental healthcare access for all Thai citizens. Additional schemes include the Civil Servant Medical Benefit Scheme (CSMBS) for government employees and the Social Security Scheme (SSS) for those in the private sector. In the private sector, individuals typically cover expenses out-of-pocket or through private insurance plans.
2. How do government policies influence healthcare access and affordability for different demographics?
The government has taken various steps to enhance accessibility and affordability in healthcare. In addition to introducing targeted schemes like CSMBS and SSS, vulnerable groups such as the elderly and children receive subsidies and financial aid to improve affordability. Telemedicine has been implemented in remote areas, ensuring that even rural patients can access healthcare consultations. A recent initiative, the “Treatment Anyway” model, allows UC beneficiaries to utilize healthcare services at their designated primary care facilities and registered private hospitals under the NHSO. Furthermore, UC beneficiaries have access to healthcare services at pharmacies, private clinics, and private laboratories.
3. What are the major trends in healthcare insurance plans, especially concerning coverage, premiums, and reimbursement?
The predominant trend in insurance plans is the emergence of high-net-worth plans, which offer increased maximum coverage and extend to cover high-cost treatments and prevention measures. Additionally, these plans often include international provider services, catering to the needs of individuals seeking healthcare abroad. Conversely, there’s a growing trend of coverage limitations, such as deductibles and copayments, being introduced in insurance plans.
4. How are emerging technologies and data analytics transforming the management of government policies and insurance plans in healthcare?
Significant improvements in data management have been observed, particularly in addressing two of the most challenging areas: medical abuse and fraud, including duplicated claims. Artificial intelligence (AI) plays a crucial role in supporting efforts to identify and mitigate fraudulent and abusive behaviors, thereby reducing unnecessary healthcare expenditures. However, effective cooperation between the private and public sectors to facilitate data sharing remains a key challenge for success.
5. In what ways can government policies and insurance plans be tailored to prioritize patient-centric care and outcomes?
Starting with the right attitude is crucial, with both sides recognizing each other as partners in providing financial support for healthcare services and jointly responsible for controlling medical inflation to ensure future healthcare sustainability. A promising initial step could involve establishing medical standards and reimbursement processes collaboratively. By doing so, providers can be incentivized to deliver optimal medical services while minimizing the risk of fraud and abuse.
6. How do you foresee upcoming policy changes impacting the healthcare industry, particularly in terms of patient care and operational dynamics?
Two significant shifts in the healthcare landscape, namely medical inflation and digital transformation, necessitate policy changes to effectively address these challenges. To tackle medical inflation, policies may need to incorporate limitations on medical services. Even if a treatment is highly effective clinically, it should undergo a cost-benefit analysis to determine its reimbursement eligibility. While this approach may impact individual patient care quality, it aims to ensure that healthcare resources are allocated efficiently to treatments with the greatest overall benefit to society.
Regarding digital transformation, policies must adapt to accommodate the rapid advancements in technology, especially in data sciences. Every healthcare payer should be prepared to embrace and integrate new technologies into their systems to harness the potential benefits of digital innovation.
7. What economic factors influence the design and implementation of government policies and insurance plans in healthcare?
General inflation and medical inflation indeed serve as key factors influencing policy implementation in healthcare. Controlling the costs associated with new technologies and medications, as well as addressing emerging diseases like COVID-19, presents significant challenges.
8. What legal and ethical challenges arise when navigating the intersection of government policies and insurance plans in healthcare?
Navigating the legal complexities of privacy acts is indeed challenging, particularly concerning fraud and abuse detection, which requires data sharing between public and private sectors. Even with consent mechanisms in place, concerns persist among payors and providers regarding compliance with acts like PDPA.
Ethical challenges are also evident, particularly regarding reimbursement protocols. While ideally, individuals should be able to use both their basic welfare like Universal Coverage (UC) and private insurance they've paid for, the current government stance appears to encourage using private insurance first to conserve resources for those without private coverage.
9. How do healthcare organizations ensure data privacy and security while complying with government regulations and insurance requirements?
Ensuring data privacy and security hinges on two critical factors: consent and IT security controls. Implementing robust consent mechanisms is essential to safeguarding data privacy. While communication and change management efforts to educate individuals about consent entail significant work, recent years have seen increased familiarity and acceptance of consent practices among the public.
10. How can stakeholders collaborate more effectively to address gaps and improve outcomes in healthcare policy and insurance coverage?
Regulators, spanning both private and public sectors, are pivotal stakeholders in enhancing outcomes. Clear directives from bodies like the Ministry of Public Health, Medical Council, and Office of Insurance Commission (OIC) are crucial for controlling fraud and abuse, thereby mitigating medical inflation.
11. What role do digital platforms, telemedicine, and telehealth play in shaping the future of healthcare delivery under existing policies and insurance models?
Telemedicine undoubtedly enhances healthcare accessibility, although it may entail trade-offs such as overutilization and clinical risks due to encounter limitations. From an insurance standpoint, the potential cost reduction stemming from decreased inpatient and outpatient hospital visits could outweigh the increased frequency of telemedicine services.
12. How can healthcare providers and insurers encourage innovation adoption while maintaining regulatory compliance and patient satisfaction?
Engaging regulators in discussions between providers and insurers from the outset ensures compliance with regulations when implementing innovations. Additionally, conducting patient surveys during the planning phase, led by providers and insurers, serves as a valuable tool to assess patient satisfaction.
13. Based on our discussion, what do you believe are the key takeaways for healthcare leaders, policymakers, and insurance providers to navigate and optimize their strategies within the evolving healthcare landscape?
Medical inflation poses a significant threat to healthcare sustainability. Standardizing procedures is paramount at this juncture. This entails establishing uniform criteria for clinical practices, medical expenses, and reimbursement processes, aligning as closely as feasible across all payment systems.